Our Patient Research Involvement Movement (PRIME) started in April 2021 with the aim of providing and improving the standard of patient and public involvement and engagement (PPIE) in brain tumour clinical research.
PPIE means utilising the insight and knowledge of the patient and caregiver community in the design of new research through various forms of ongoing communication and review. This ensures new trials and studies have the patient needs woven in, making treatments more comfortable and supportive.
Now in its third year, PRIME continues to offer top level support to researchers and clinicians. Together we’re bridging the gap between the clinical community and the patient and caregiver community, enabling the patient voice to be in the DNA of trial and treatment design.
If you are a researcher or clinician and want to find out more about how PRIME can support your research, please contact adam@brainstrust.org.uk.
Growing the Patient Research Involvement Movement
We have a growing community of research advocates, offering their unique insights in direct discussions with neurologists, neurosurgeons and neuro-oncologists. Collectively they aim to improve the quality of life for people diagnosed with a brain tumour.
Taking on a yet more involved role in the research landscape, our research partners have been attending our regular training sessions – exploring and learning about the research landscape, what makes good PPI, and the challenges we want to overcome together.
Right now, we have:
- Begun training 23 Research Partners in how to deliver top-level patient involvement,
- Recruited 77 Research Advocates who help researchers shape trials and studies to improve care for future patients,
- Signed up over 800 people to our Monthly Brew research newsletter, providing knowledge and news about the field.
Pushing the standards of patient involvement
As our service continues to reach more people in clinical spaces, we are getting involved in some wonderful, forward-thinking research.
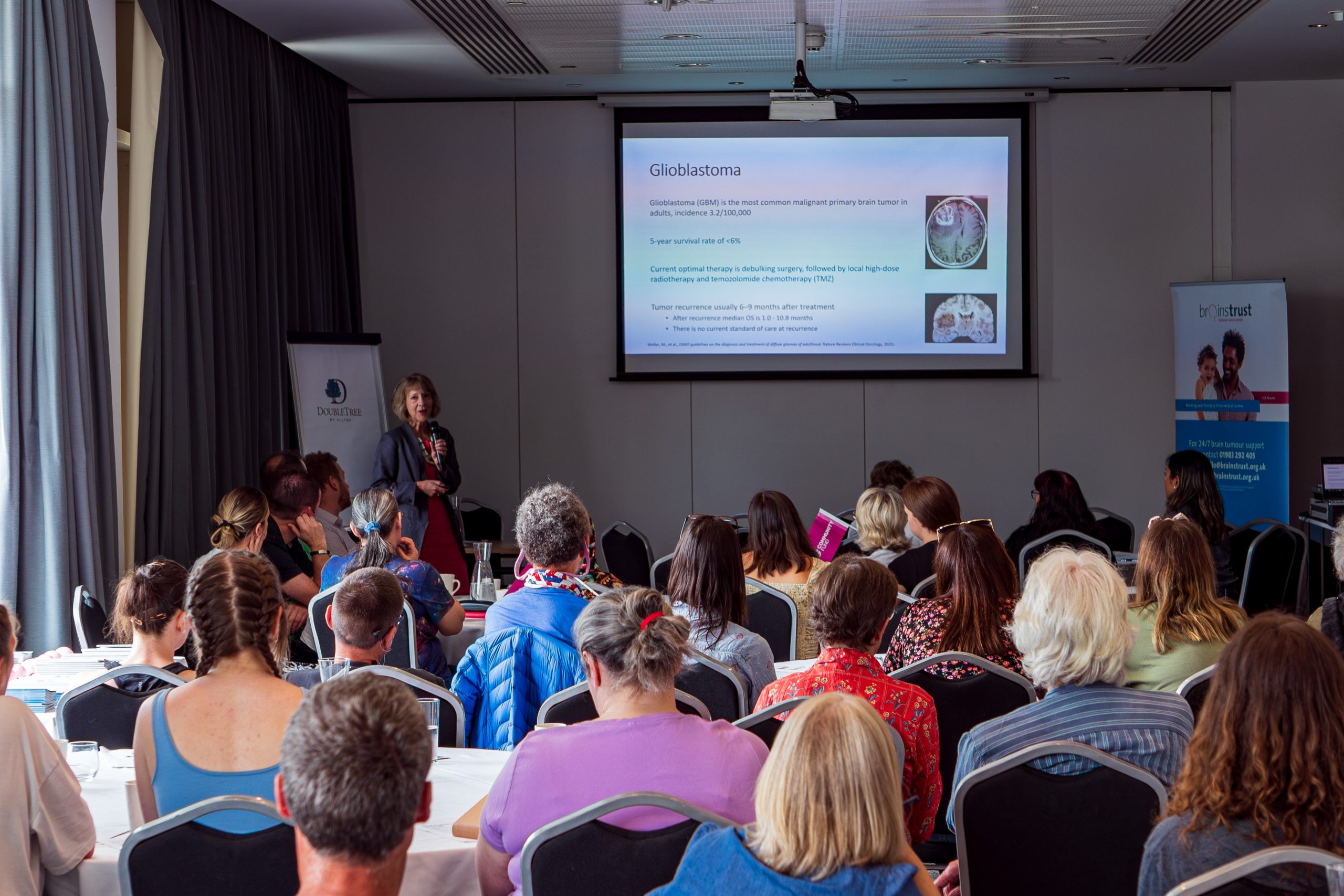
The clinical research community is investigating all angles when it comes to improving quality of life and life expectancy after a brain tumour diagnosis. Helping improve the standard of so many of these studies and trials comes gives us the motivating responsibility to continue pushing the standards of patient involvement.
Some of the aims we’ve helped researchers achieve include:
- Creating core outcome sets
- Gathering feedback on pathway proposals
- Analysing diagnosis preferences
- Determining issues with current treatment
- Identifying areas for improvement on trial design
- Suggesting new methods of support for patients
- Making research accessible
- Providing unique perspective

PRIME has also been sharing news and insight through our research-focused newsletter: The Monthly Brew (formerly the Weekly Brew). Regardless of the frequency of brews per month (BPM?), the newsletter is reaching a growing number of research hungry members of the community. It provides opportunities to be involved, highlights from various studies and any need-to-know information about what’s happening at the forefront of the clinical landscape.
Want to receive all the latest research straight to your inbox?
Sign-up our curated, jargon-free weekly research newsletter. Click here to fill out our contact form and select ‘research’ to opt into our research newsletter.
Other PRIME news and the future
Over the past year we have strengthened our partnership with Brain Tumour Research. Their support has given PRIME even more capacity to support and provide PPI to current research. Our goal of improving outcomes by contributing to clinical trial design are aligned, and we look forward to continued collaboration to push this gold standard further.
We are also supported by Naseem’s Manx and Brain Tumour Charity, a fantastic charity providing brain tumour support to the Isle of Man community.
We are grateful and proud to have relationship with such passionate and inspiring organisations.
Looking ahead, we will continue to provide our support to more exciting and important projects. Together we can transform the care available for anyone affected by a brain tumour, helping them live their best life possible after diagnosis.
Join the movement
If you would like to use your experience and insight to support clinical research, consider signing up to be a PRIME advocate for brainstrust.
If have any questions about PRIME, or want to access support, call us on 01983 292 405 or email hello@brainstrust.org.uk. You can also visit our little brainstrust website which features support for children affected by brain tumour.