On Friday 9 June patients, caregivers, health professionals and local organisations joined us for a day of connection and empowerment at Thrive with brainstrust in Brighton. The day brought opportunities for sharing experiences, connecting with others, learning from speakers, building resilience, and improving wellbeing.
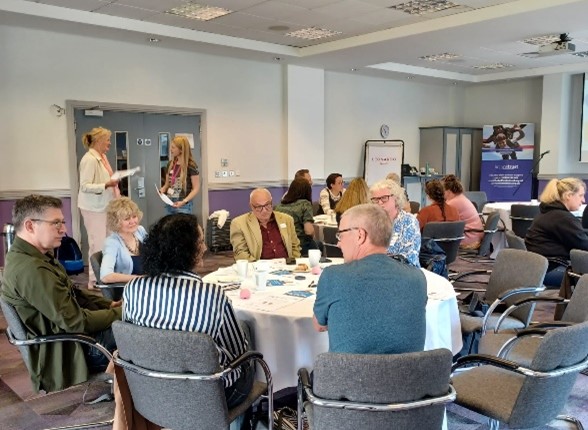 We started the day with a peer networking session introduced by one of our fantastic peer supporters, Andy. Andy spoke about his experiences of receiving peer support and now volunteering as a peer supporter himself. The session allowed everyone to share what had brought them along to the day and what their brain tumour journey has looked like so far. The group discussion was incredibly supportive and lots of connections were made between attendees as they spoke with others who really got it.
We started the day with a peer networking session introduced by one of our fantastic peer supporters, Andy. Andy spoke about his experiences of receiving peer support and now volunteering as a peer supporter himself. The session allowed everyone to share what had brought them along to the day and what their brain tumour journey has looked like so far. The group discussion was incredibly supportive and lots of connections were made between attendees as they spoke with others who really got it.
“Everyone was in the same boat and I didn’t have to keep explaining things. I felt normal for the first time since my diagnosis.” – Patient
 Jane Rose-Land, a Nutritionist who regularly features on our online events calendar, kindly travelled down from Norfolk to be the morning keynote speaker. Jane started the day with an interesting talk around the how and why of blood sugar management and keto diets. Dr Bindemann, who was speaking later in the day, also brought along some tasty keto treats to try in the break to show everyone what can be achieved with baking without sugar and kindly brought along recipe bags for everyone to take home and give keto baking a try themselves!
Jane Rose-Land, a Nutritionist who regularly features on our online events calendar, kindly travelled down from Norfolk to be the morning keynote speaker. Jane started the day with an interesting talk around the how and why of blood sugar management and keto diets. Dr Bindemann, who was speaking later in the day, also brought along some tasty keto treats to try in the break to show everyone what can be achieved with baking without sugar and kindly brought along recipe bags for everyone to take home and give keto baking a try themselves!
“It was so helpful to hear the info sessions and meet others going through their journey. We can’t thank you enough.” – Caregiver
We were then joined by our Co-Founder and Director of Services and Policy at brainstrust, Dr Helen Bulbeck, who talked about what’s at play in the brain tumour landscape and how to get involved with our PRIME programme.
“Now, more than ever, people want to be closer to research so that they can feel engaged with their care and their condition, ensuring that they understand the landscape and that they aren’t missing out.” Dr Helen Bulbeck, brainstrust
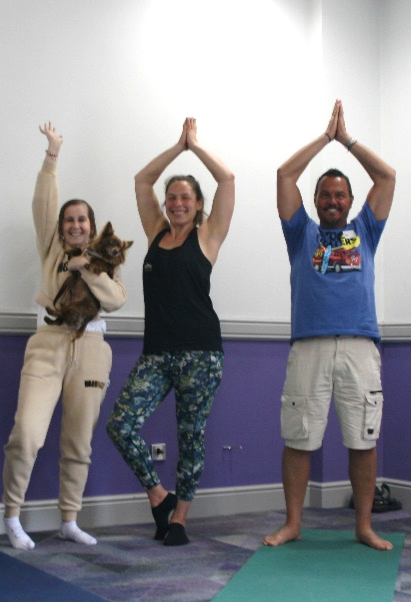 Alongside two of the morning sessions was Yoga, run by Xenia, a local yoga instructor from BrightonYoga. Xenia made the sessions very accessible, helping those who attended to re-centre and unwind.
Alongside two of the morning sessions was Yoga, run by Xenia, a local yoga instructor from BrightonYoga. Xenia made the sessions very accessible, helping those who attended to re-centre and unwind.
“It was great seeing so many people making really valuable connections with those around them, scribbling down information that was meaningful to them from what the speakers were saying and un-winding in the yoga sessions.” – Molly, brainstrust
One of our fantastic brainstrust volunteers, Damon, kicked off the afternoon speaking about learning to adapt + flow with life when you’ve been diagnosed with a brain tumour. Damon shared reflections on his journey and what’s made all the difference for him along the way.
Dr Neil Bindemann then joined us to speak about person-centred lifestyle health solutions; exploring what it means be trauma informed, emotional health and the impact of hearing life altering medical news.
“Thank you very much for putting on a great day and for providing so many useful tools and informative sessions from all types of areas impacting brain injury.” – Caregiver
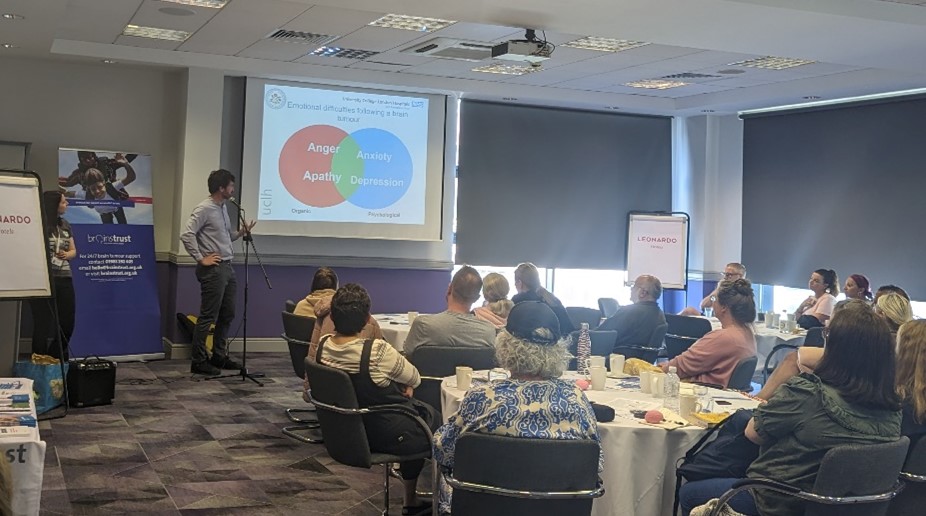 Alongside this Laura, brainstrust support specialist for central south England, ran a fatigue workshop. Laura talked through the impacts of brain tumour related fatigue and some strategies to help manage this.
Alongside this Laura, brainstrust support specialist for central south England, ran a fatigue workshop. Laura talked through the impacts of brain tumour related fatigue and some strategies to help manage this.
The day finished with Dr Patrick Murphy, our afternoon keynote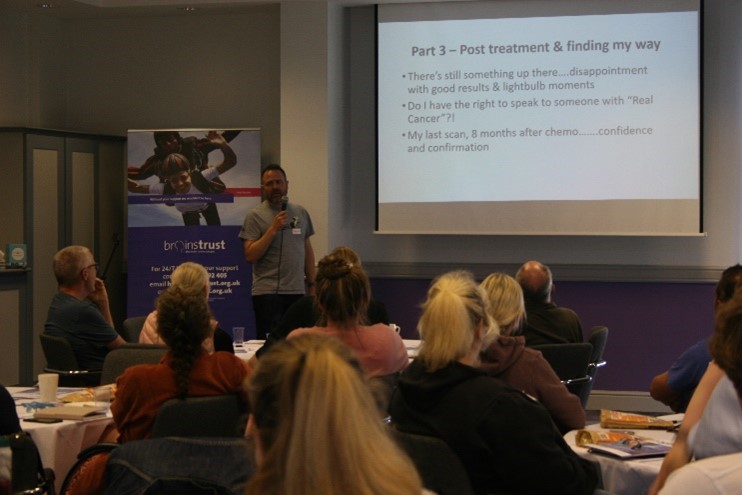 speaker who had kindly travelled down from UCLH in London to talk about working with behaviour and emotional changes. Dr Murphy was able to talk about his years of experience working as a Principal Clinical Neuropsychologist to explore managing executive function and emotional difficulties for those living with a brain tumour.
speaker who had kindly travelled down from UCLH in London to talk about working with behaviour and emotional changes. Dr Murphy was able to talk about his years of experience working as a Principal Clinical Neuropsychologist to explore managing executive function and emotional difficulties for those living with a brain tumour.
“It was so great for Molly and I to meet so many members of our community in person and so brilliant to see connections forming and strengthening. I had so many inspiring conversations during the day and took away such fantastic ideas for future brainstrust events and projects.” – Laura, brainstrust
I extend big thank you to everyone who came along to the event and to all of our wonderful speakers and volunteers that helped to make the day so interesting and accessible.
volunteers that helped to make the day so interesting and accessible.
Thrive with brainstrust wellbeing days is a series of events that will be popping up across the UK over the coming year. Visit our eventbrite page to find out more about upcoming events.
Hope to see you at one of our events soon!
Molly
Support Specialist for London and the south east, brainstrust
molly@brainstrust.org.uk